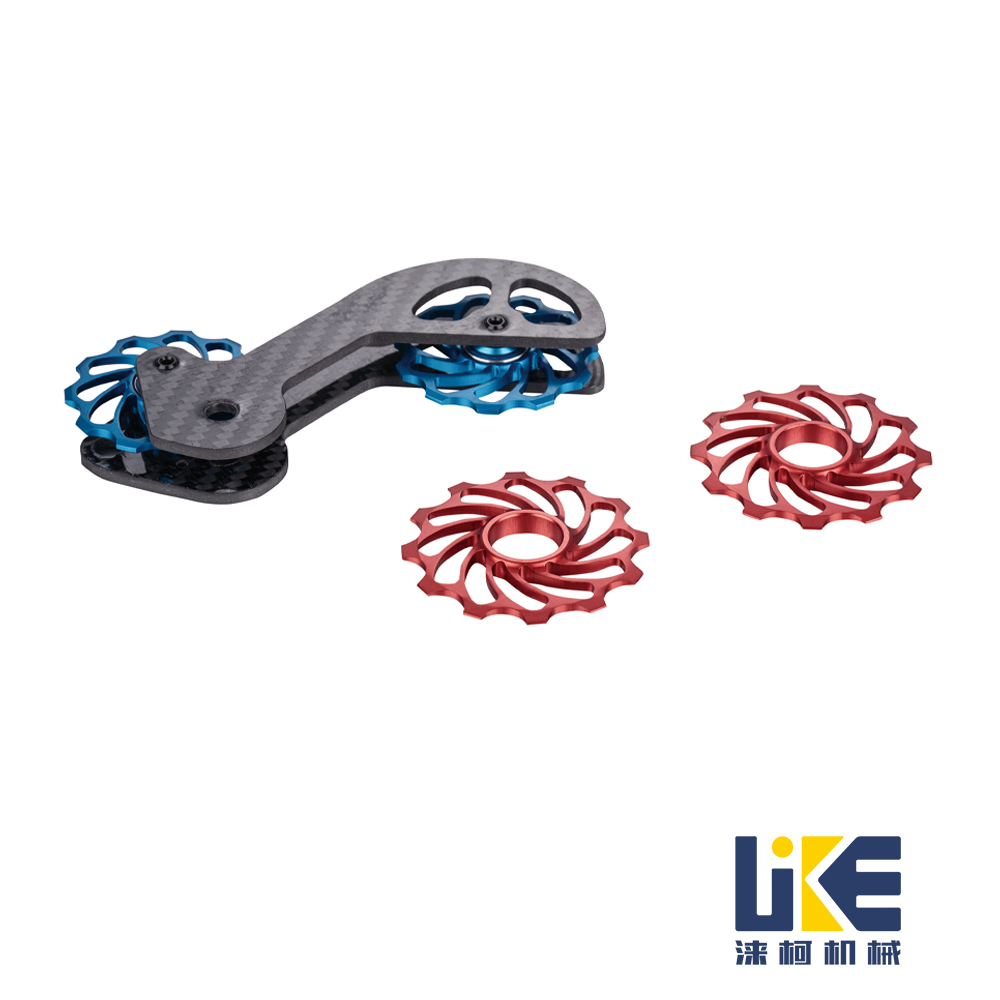

Bicycle derailleur guide pulley
Bicycle rear derailleur guide pulley
The rear transmission guide wheel (often referred to as the guide wheel or tension wheel) is a core component of the rear chain drive mechanism. Its main function is to ensure a stable path for the chain when shifting gears on the flywheel, and to maintain the appropriate tension of the chain by cooperating with the spring tension of the chain drive mechanism, thereby ensuring precise shifting and efficient power transmission.
Structure and Working Principle: The guiding wheel is usually composed of an upper guiding wheel (idler wheel) and a lower tension wheel. Both are designed with high-precision ball bearings to reduce rotational resistance, and are made of high-strength wear-resistant materials to balance lightweight and durability. When the rider operates the gear shift handle, the rear chain drive mechanism moves, and the guiding wheel adjusts its position accordingly, guiding the chain to smoothly transition from the current freewheel teeth to the target teeth, while avoiding chain slack or shaking.
Key Functions and Impacts: The steering wheel directly affects the performance of the transmission system, specifically including:
Improve shifting smoothness: Smooth bearing rotation can reduce shifting jolts, especially in mountain bikes or road bikes that frequently change gears.
Reduce chain jumping risk: By precisely guiding the chain, it lowers the possibility of chain detachment during high-speed pedaling or climbing.
Extend transmission system lifespan: Stable tension and reduced friction help protect components such as the chain and flywheel.
Adapt to complex road conditions: Design features like rust prevention can enhance reliability in adverse conditions such as rainy days.
Maintenance and Adjustment Key Points: Regular cleaning of the guide wheels and lubrication of the moving parts are crucial for maintaining their performance. If there is any abnormal noise or wear, the guide wheels may need to be replaced. When making adjustments, the following aspects should be paid attention to:
Limiting screws: The screws marked "H" control the minimum distance between the guide wheel and the flywheel, and rotating counterclockwise increases the spacing; the screws marked "L" control the distance from the largest teeth.
B Tension adjustment bolt: Used to adjust the parallel spacing between the guide wheel and the flywheel. The ideal distance is 5 to 10 millimeters. Too close may cause collision noise, and too far may affect the shifting speed.
Alignment check: When the chain operates in each gear position, the guide wheel should be in the same vertical plane as the corresponding flywheel teeth; otherwise, it is prone to chain breakage.

Can produce any components for the bicycle industry, such as screws and transmission brackets.


