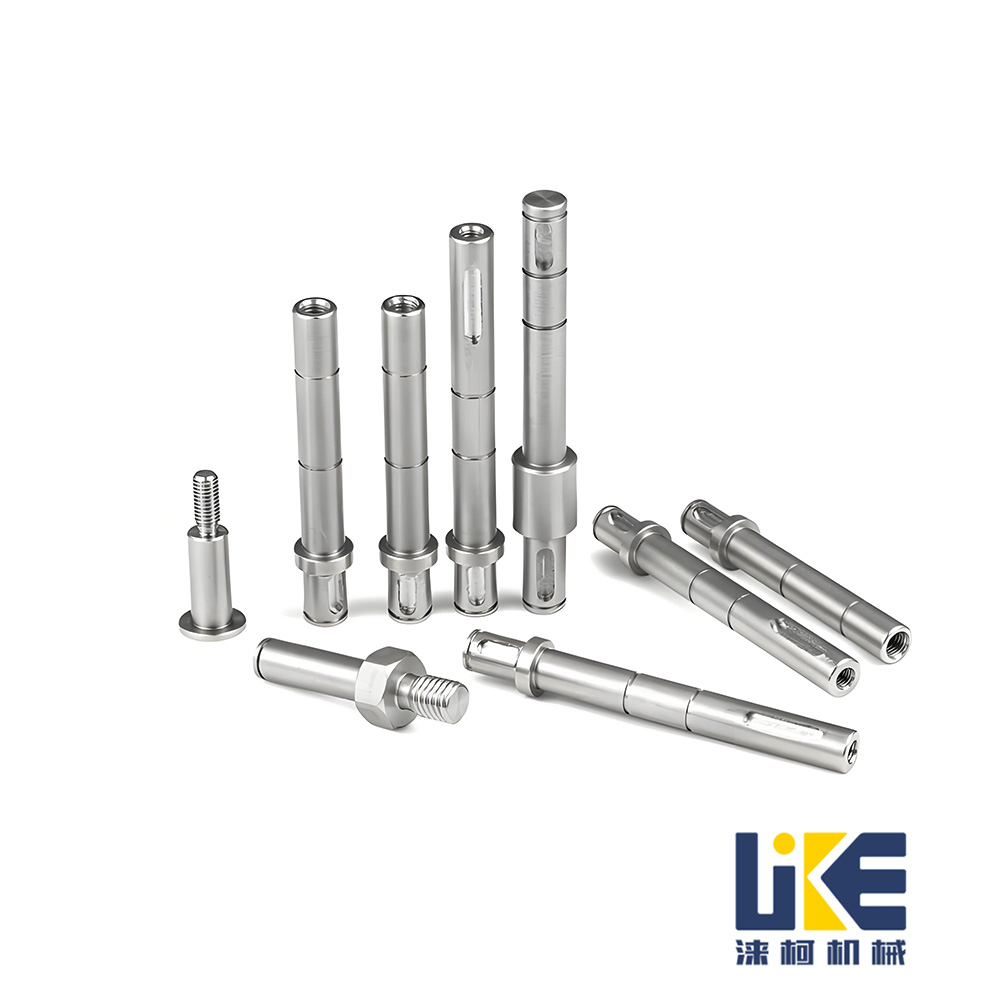
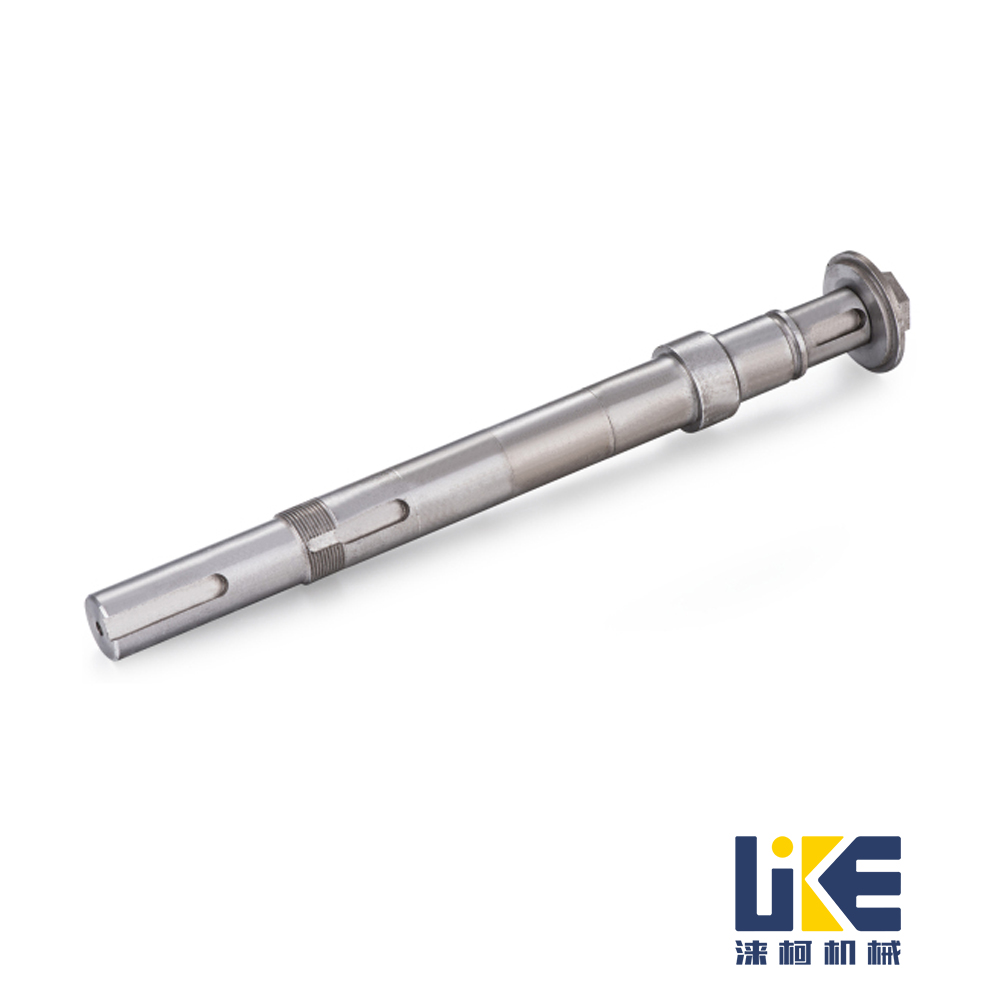

locating pin,cylinder pin
Classification of Positioning Pins
As a key component used for precise positioning in mechanical design and manufacturing, positioning pins can be classified based on dimensions such as structure, function, and application scenarios. They can be divided into the following categories (the core classification is based on "cylindrical pins, conical pins, and slotted pins", and other types are extended):
1. Core basic classification (most common, standardized)
Cylindrical pins:
Have a simple cylindrical structure and achieve radial positioning by mating with the hole of the workpiece. The advantages are simple structure, convenient processing, and low cost; however, they cannot prevent the workpiece from rotating around the pin.
Example: In the processing of automotive engine cylinder blocks, cylindrical pins are used to position bolt holes to ensure consistent processing positions.
Cone Pin:
A conical structure with a 1:50 taper. It can be easily tightened by tapping during installation and easily disengaged during removal. It is widely used in scenarios where frequent assembly and disassembly are required, such as in machine tool fixtures.
Example: In machine tool fixtures, the cone pin achieves rapid positioning and disassembly of the workpiece through "self-locking by taper".
Screw Pin:
The surface is equipped with spiral grooves, similar to "anti-slip patterns", which can firmly grip the hole wall through friction. It is suitable for scenarios with high vibration and requiring high vibration resistance (such as agricultural machinery equipment).
Example: In agricultural machinery equipment, the screw pin relies on friction to stably hold the workpiece, preventing loosening caused by vibration.
2. Expanded Classification (Subdivision by Function/Structure)
Activity Positioning Pin:
After installation, it can move slightly, accommodating minor errors during the assembly process.
Example: In the automotive body assembly line, the activity positioning pin ensures precise alignment of each part before welding.
Locking type positioning pin:
Equipped with a locking mechanism to prevent the pin body from accidentally falling off. Suitable for high-vibration environments (such as in the aerospace field).
Example: In the connection between the aircraft fuselage and the wing structure, the locking type positioning pin ensures a stable connection under extreme conditions.
Special-shaped locating pins:
Complex in design (such as pins with inclined surfaces), suitable for specific working conditions (such as robotic arms, automatic assembly lines).
Example: In complex robotic arms, special-shaped locating pins provide precise positioning and support.
Small locating pin:
Small in size, used for local fixation, providing lightweight support.
Example: In precision mechanical structures, small locating pins ensure precise positioning of components.
Fixed Positioning Pin:
It cannot be moved. As a fixed device in the structure, it ensures stability.
Example: In vehicle manufacturing, the fixed positioning pin ensures that key components do not move randomly, guaranteeing driving safety.
Replaceable Positioning Pin:
It offers flexibility for replacement and is suitable for scenarios where adjustments or replacements need to be made frequently (such as in mold manufacturing).
Example: During mold maintenance, the replaceable positioning pin makes it easy to quickly replace worn components.
Positioning Pin:
Inserted into the hole with a unique design, it provides rigidity and precise positioning.
Example: In complex mechanical structures, the positioning pin ensures the precise position of key components.
3. Other classification dimensions (such as "fixed/active" and "replaceable/irreplaceable")
Fixed positioning pin: Cannot be moved. It serves as a fixed device in the structure to ensure stability.
Replaceable positioning pin: Has flexibility for replacement. It is suitable for scenarios where frequent adjustments or replacements are required (such as mold manufacturing). Summary
The classification of locating pins should be understood from multiple dimensions such as structural form, functional characteristics, and applicable scenarios: the core basic classification is "cylindrical pins, conical pins, and slot pins", and the expanded classification includes "moving/locking/special shapes/small/fixed/replaceable/locating pins" and so on. Different classifications correspond to different positioning requirements in different working conditions, and they are key components for achieving precise assembly in mechanical design.


