Information technology and metal stamping parts
IT industry's requirements for stampings typically focus on miniaturization, high precision, electromagnetic shielding, and large-scale mass production capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of their specific functions:
1. Electromagnetic Shielding (EMI Shielding) – One of the most critical functions
IT equipment is filled with high-frequency signals (CPU, Wi-Fi, 5G, Bluetooth), which are prone to interference.
Function: Prevents electromagnetic wave leakage from interfering with other devices, while also preventing external signals from interfering with the stable operation of internal chips.
Specific products:
Shielding Cans: Tiny metal covers soldered onto the motherboard, covering the CPU, memory, or RF chips. Typically made of nickel silver or stamped tinplate.
Interface Housings: Metal housings for USB, HDMI, and RJ45 network ports, serving both a fixing function and grounding shielding.
2. Structural Chassis & Enclosures
This is the most basic function of stamped parts: providing a mounting platform and protection for electronic components.
Function: Secures components such as motherboards, power supplies, and hard drives, providing physical protection against impacts and compression.
Specific Products:
Server Chassis: The enclosure of 1U/2U/4U servers in data centers, almost entirely made of galvanized steel sheet through stamping and bending.
Desktop Chassis: The main frame of a computer.
Laptop Internal Bracket: Keyboard backplate, motherboard bracket, hinge (rotary hinge) assembly.
Mid-plate: A metal partition between the phone screen and motherboard, used to enhance the rigidity of the device and prevent bending.
3. Precision Connectors & Terminals
IT equipment requires frequent data transmission and charging, relying on countless tiny metal contact points.
Function: Ensures stable transmission of current and signals, requiring extremely high wear resistance and elasticity (mating/removing life).
Specific Products:
USB Type-C Interface Components: Internal tiny spring contacts and external stretching housing.
CPU Socket: The metal clip that holds the CPU in place.
Memory/Graphics Card Slot Clips: And their internal conductive spring contacts.
Battery Connector: Mobile phone battery contacts, typically made of beryllium copper stamping, offering good conductivity and high elasticity.
4. Thermal Management
While the main heatsink is made of extruded or die-cast aluminum, stamped components also play a role in the cooling module.
Function: Conducts heat, increasing the heat dissipation area.
Specific Products:
Heat Stacks: The thin metal sheets at the ends of laptop heat pipes, usually aluminum or copper sheets fastened together by high-speed stamping (button-pressing process).
Backplate: The metal plate on the back of the graphics card or CPU, preventing PCB warping and aiding in heat dissipation.
5. Storage Components
Hard disk drives (HDDs) are the culmination of precision mechanics, requiring extremely high precision in stamping.
Function: Sealing and dustproofing, supporting the high-speed rotating platters.
Specific Products:
HDD Top Cover: Stainless steel stamping, requiring extremely high flatness and cleanliness.
Voice Coil Motor Magnet Plate: A key component inside the hard drive controlling the movement of the read/write arms.
SSD Casing: The metal protective shell of the solid-state drive (usually aluminum stamping or stainless steel).
6. Why is stamping indispensable to the IT industry?
Mass Production: Products like iPhones or Dell computers sell tens of millions of units annually. Only stamping can produce a part in seconds, ensuring that each part is perfectly sized.
Lightweighting and Thinning: As IT devices become increasingly thinner (such as ultrabooks and foldable phones), stamping can process high-strength steel or titanium alloy sheets only 0.1mm or even thinner, which is difficult to achieve efficiently with CNC machining.
Cost Control: Compared to CNC machining, stamping offers higher material utilization and faster processing speeds, significantly reducing the manufacturing costs of IT hardware.
Summary: In the IT industry, metal stampings form the foundational building blocks for everything from microscopic signal transmission (connector springs) to macroscopic physical protection (server chassis). Without precision stamping technology, modern IT equipment could not have achieved its current high integration, slim design, and low-cost widespread adoption.
 Decorative items and metal stampings
Decorative items and metal stampings
 Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
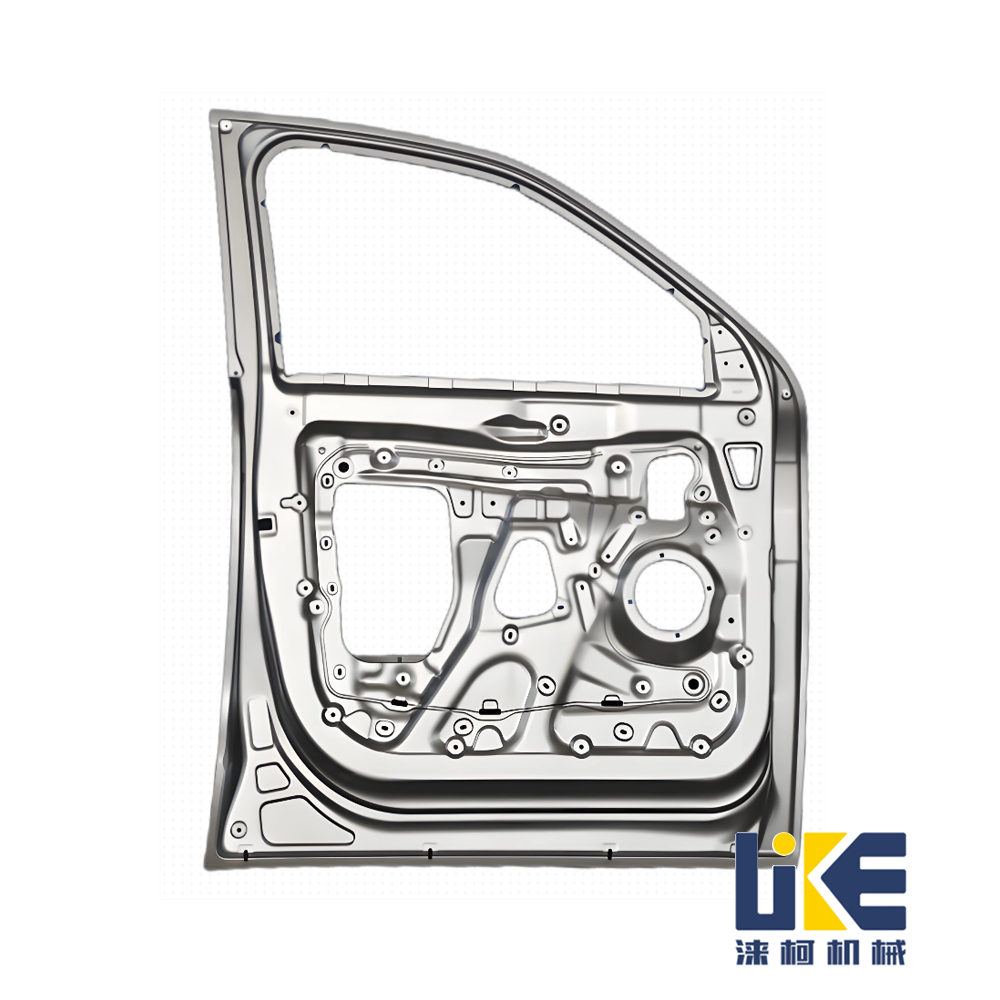 Automotive and metal stamping parts
Automotive and metal stamping parts


