Artificial intelligence and metal stamping parts
The role of metal stampings in the AI industry is primarily reflected in providing physical support and heat dissipation for the AI's "brain" (computing center), and in constructing moving parts and a framework for the AI's "body" (embodied intelligence/robots).

The specific roles of metal stampings in the field of artificial intelligence are as follows:
1. AI Computing Infrastructure (AI Servers & Data Centers):
This is currently the most core hardware area in the AI industry (such as server clusters running ChatGPT). AI servers consume more power, are heavier, and generate more heat than ordinary servers, placing new demands on stampings.
Heavy-duty Chassis & Racks:
Purpose: AI servers (such as servers equipped with NVIDIA H100 processors) are filled with heavy GPU modules and heat sinks. Stampings form the server's shell, rails, and internal supports, requiring higher load-bearing capacity and shock resistance than ordinary IT equipment.
Power Busbars:
Purpose: AI training clusters consume extremely high power. Stamped thick copper busbars are used to replace traditional cables for high-current transmission, reducing resistance and heat generation, and improving energy efficiency.
Hard Drive/Storage Array Brackets:
Function: AI training requires massive amounts of data. Stamped components are used to secure high-density SSD or HDD storage arrays, ensuring stable data access.
2. High-Performance Cooling System (Advanced Thermal Management)
AI chips (GPUs/TPUs) are notorious for generating significant amounts of heat. Poor heat dissipation can cause a sudden drop in AI computing power. Stamped components are a core part of the cooling module.
Heatsink Fins:
Function: Aluminum or copper strips are stamped at high speed to create extremely thin fins, which are then assembled using zipper fins or welding processes. This is the core of air-cooled heatsinks, used to greatly increase the heat dissipation area.
Liquid Cooling Plates:
Function: As AI power consumption exceeds the limits of air cooling, liquid cooling has become mainstream. The microchannels or sealing covers inside liquid cooling plates are often manufactured using precision stamping and brazing processes, requiring extremely high sealing and flatness.
3. Embodied AI & Robotics
When AI enters the physical world (such as humanoid robots and industrial robotic arms), stamped parts are their "muscles" and "skeleton."
Motor Laminations: (Key Applications)
Function: Every joint of a robot requires a servo motor. The core components inside the motor—the stator and rotor—are stacked from silicon steel sheets using high-speed precision stamping dies. Stamping accuracy directly affects the robot's motion accuracy and energy efficiency.
Harmonic Drive Flexspline:
Function: A core component of robot joints. Although traditionally mostly machined, current technologies use spinning or special stamping processes to manufacture thin-walled flexsplines to reduce costs and achieve mass production.
Lightweight Skeleton:
Function: Humanoid robots need to be lightweight to reduce energy consumption. High-strength aluminum or titanium alloy stamped parts are used for the torso and limbs shell, making them both lightweight and robust.
4. Intelligent Sensors & Perception Layer
AI needs to "see" the world through cameras and radar.
Automotive Radar/Camera Mounts:
Purpose: In autonomous vehicles, the metal mounts that fix LiDAR and cameras must be extremely stable and cannot shift due to vehicle vibrations, otherwise, it will lead to AI misjudgments. These are typically precision stamped parts.
EMI Shielding:
Purpose: Protects high-precision sensor chips from external electromagnetic interference, ensuring that the data received by AI is pure.
5. Edge AI Devices
AI PC / AI Phone: As AI models become smaller, edge devices require more powerful NPUs. The role of stamped parts here is similar to that in the IT industry (heat dissipation, shielding, structure), but the stamping process for **thermal vapor chambers (VCs)** is more demanding because the heat generated by edge AI increases significantly.
In summary, if we liken artificial intelligence to a "super brain": Stamped parts are the "skull": protecting expensive GPU servers and chips (chassis, casing).
Stamped parts are the "blood vessels": transmitting enormous amounts of current (copper busbars) and heat (heat sinks).
Stamped parts are the "muscle fibers": forming the core of robot motors (silicon steel stators and rotors).
In the AI industry, metal stamped parts are evolving towards higher heat dissipation efficiency, higher strength, and lighter weight, playing a crucial role in transforming AI from "virtual algorithms" into "physical entities."
 Decorative items and metal stampings
Decorative items and metal stampings
 Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
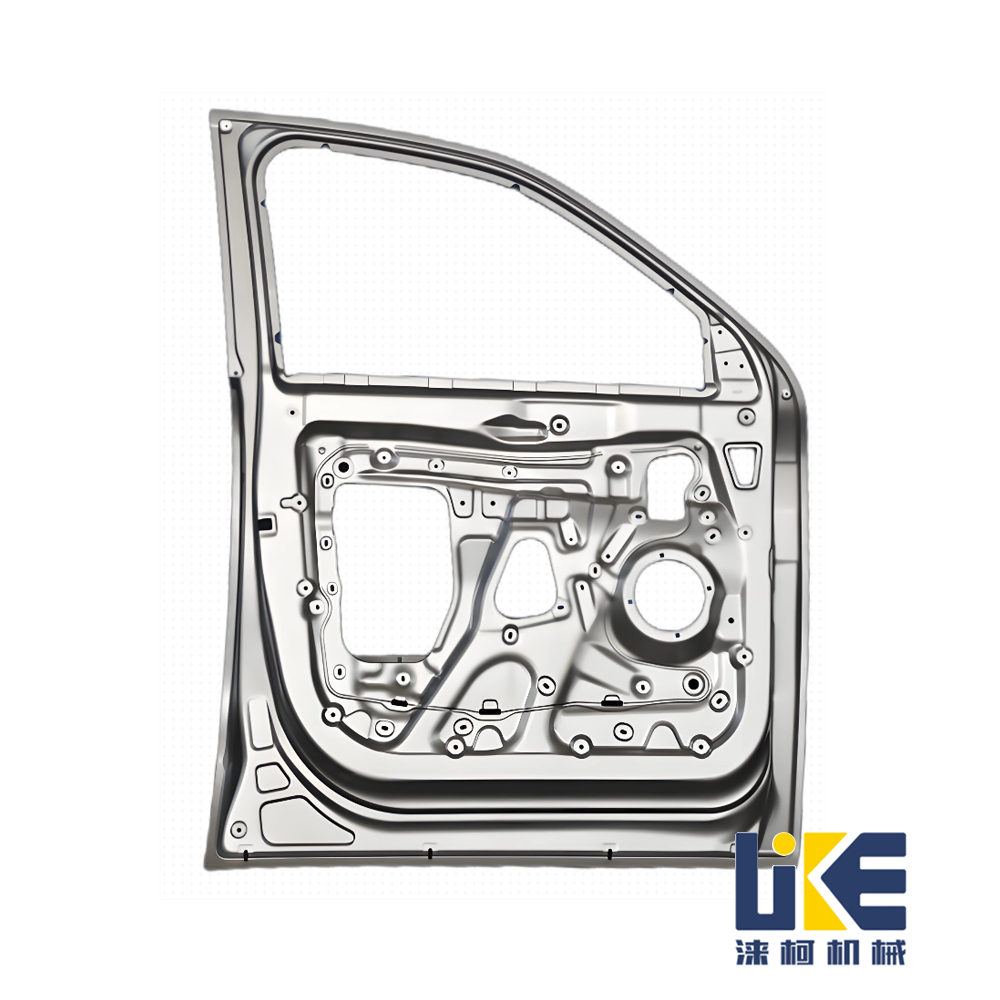 Automotive and metal stamping parts
Automotive and metal stamping parts


